Copper mines, exemplified by Rio Tinto’s Bingham Canyon mine on the outskirts of Salt Lake City, occupy a pivotal role in America’s shift toward clean energy. As the demand for copper, a fundamental component of electric vehicles, is projected to surge from 25 million metric tons to nearly 49 million metric tons by 2035, according to S&P Global, these mining operations find themselves at the forefront of an industry grappling with multifaceted challenges.
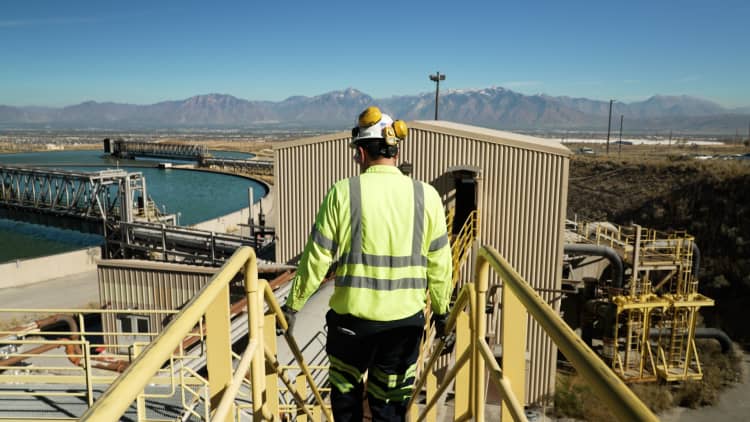

The growth trajectory in copper production faces an array of complexities, ranging from appeasing local stakeholders and mitigating environmental impacts to operating in geographically isolated regions across the globe. Tyler Broda, a metals and mining analyst at RBC Capital Markets, emphasizes the looming challenges for companies in maintaining current production levels, anticipating a genuine struggle over the next decade.
Rio Tinto, a mining giant with a global footprint and dual headquarters in Australia and the UK, is strategically positioned to navigate these challenges. With projects spanning 35 countries, Rio Tinto boasts 17 iron ore mines in Western Australia, contributing to steel production, alongside ventures in aluminum, diamonds, and boron—an essential component in smartphones.
Offering a glimpse into Rio Tinto’s critical minerals business, CNBC delves behind the scenes of the company’s Utah operation to unravel the strategies employed in the pursuit of ramping up production. The exploration of Rio Tinto’s endeavors provides insights into the innovative approaches and technologies harnessed by mining industry leaders as they navigate the intricate landscape of sustainable resource extraction amid surging demand and evolving environmental considerations.