In today’s global economy, various economic systems are in place, each with its own unique features and characteristics. One such system is a mixed market economy, which combines elements of both a market economy and a planned economy. This blend allows for a balance of governmental control and individual autonomy in economic decision-making. In this blog post, we will explore the definition of a mixed market economy, its key features, the role of government within it, as well as its advantages and disadvantages. By examining these aspects, we can gain a better understanding of how a mixed market economy operates and its impact on individuals and businesses within a society. Whether you are a student of economics or simply curious about different economic systems, this post will provide valuable insights into what a mixed market economy entails and how it functions in today’s world.
Definition of a mixed market economy
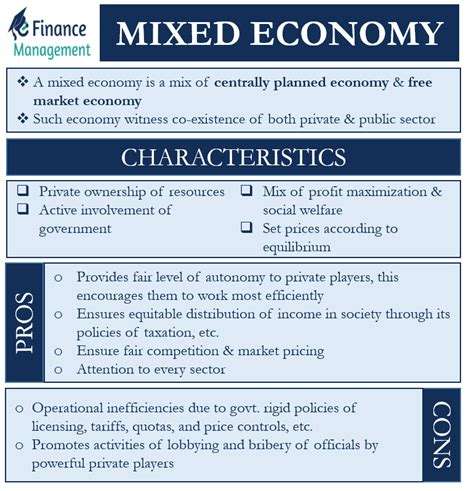
A mixed market economy is an economic system that incorporates elements of both a free market economy and a planned economy. In this system, private individuals and businesses have the freedom to own and control the means of production, while the government also plays a significant role in regulating and controlling certain aspects of the economy. It is characterized by the coexistence of private enterprise and government involvement, allowing for a combination of capitalism and socialism.
One of the defining features of a mixed market economy is the presence of both a private sector and a public sector. The private sector consists of privately-owned businesses and individuals who operate in pursuit of profit, while the public sector includes government-run organizations and services that are focused on the welfare of the society. This combination allows for a balance between individual freedom and social welfare, aiming to achieve economic growth and social equity simultaneously.
In a mixed market economy, the government plays a crucial role in ensuring fair competition and preventing market failures. It regulates various industries, enforces antitrust laws, and provides public goods and services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. Additionally, the government also implements fiscal and monetary policies to manage the overall performance of the economy, aiming to control inflation, unemployment, and economic stability.
Overall, a mixed market economy is defined by its hybrid nature, combining elements of both market-driven and centrally planned economic systems. It seeks to achieve a balance between individual freedom and collective responsibility, allowing for economic efficiency and social welfare to coexist. This economic model aims to address the limitations of both pure capitalism and pure socialism, providing a flexible and adaptable approach to economic organization.
Features of a mixed market economy
Flexibility: One of the key features of a mixed market economy is its flexibility. This means that the market can adapt to changing circumstances and respond to consumer demands and preferences. As a result, businesses have the freedom to innovate and diversify their offerings to meet the needs of the market.
Competition: In a mixed market economy, competition is encouraged and valued. The presence of multiple competing businesses helps drive innovation and efficiency, leading to better products and services for consumers. This competitive environment also helps keep prices in check, preventing monopolies from dominating the market.
Regulation: Despite the emphasis on free market principles, a mixed market economy also incorporates elements of government regulation. This can take the form of laws and regulations designed to protect consumers, prevent fraud, and ensure fair labor practices. Regulation helps maintain a level playing field and promotes ethical business conduct.
Public Goods: Mixed market economies often involve the provision of public goods and services by the government. This may include infrastructure, public education, healthcare, and social welfare programs. By providing these essential services, the government can address market failures and help ensure broader access and equity in society.
The role of government in a mixed market economy
In a mixed market economy, the role of government is crucial in maintaining a balance between the free market forces and government intervention. The government plays a significant role in regulating and overseeing the economy to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, and the overall stability of the market. One of the primary functions of the government in a mixed market economy is to establish and enforce regulations that prevent monopolies and promote healthy competition among businesses. This helps to prevent the concentration of economic power in the hands of a few large corporations, which could negatively impact consumer choice and market efficiency.
Additionally, the government in a mixed market economy is responsible for providing public goods and services that the private sector may not adequately supply. This includes infrastructure development, national defense, education, healthcare, and social welfare programs. By investing in these areas, the government aims to improve the overall quality of life for its citizens and ensure that essential services are accessible to all members of society, regardless of their financial means.
Furthermore, the government also plays a role in addressing externalities, such as pollution and environmental degradation, through the implementation of environmental regulations and policies. This helps to internalize the social costs of production and consumption, promoting sustainable growth and ensuring that businesses take responsibility for the negative external impacts of their activities.
Overall, the role of government in a mixed market economy is multifaceted, encompassing regulatory oversight, provision of public goods, and addressing market failures. By striking a balance between free market dynamics and government intervention, a mixed market economy aims to promote economic growth, social welfare, and a fair distribution of resources.
Advantages of a mixed market economy
A mixed market economy is a system that combines aspects of both free market and command economies. In this type of economy, individuals and businesses have the freedom to make economic decisions, while the government also plays a significant role in regulating and controlling certain aspects of the economy.
One of the key advantages of a mixed market economy is that it allows for both economic freedom and government intervention. This means that individuals and businesses have the freedom to pursue their own economic interests, while the government can step in to address issues such as market failures, income inequality, and externalities.
Another advantage of a mixed market economy is economic stability. By combining elements of both free market and command economies, this system is better able to mitigate the fluctuations and uncertainties that are often associated with purely free market or command economies.
Additionally, a mixed market economy can promote innovation and competition. With a balance of economic freedom and government intervention, this type of economy can create an environment where businesses are incentivized to innovate and compete, leading to overall economic growth and development.
Disadvantages of a mixed market economy
One of the disadvantages of a mixed market economy is the potential for inequality. Because this type of economy allows for both private and public ownership, there is a risk that wealth and resources may become concentrated in the hands of a few individuals or corporations. This can lead to a widening wealth gap and socioeconomic disparities within society.
Another disadvantage is the potential for government intervention to create inefficiencies. In a mixed market economy, the government plays a role in regulating and controlling certain aspects of the market. However, excessive or mismanaged government intervention can lead to red tape, bureaucracy, and market distortions, which can impede economic growth and innovation.
Additionally, a mixed market economy may be susceptible to market failures. While the private sector is allowed to operate freely, there are instances where the market may not efficiently allocate resources, leading to inefficiency and suboptimal outcomes. This can result in issues such as externalities, imperfect competition, and public goods undersupply.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of a mixed market economy can also be a disadvantage. The constant interplay between the private and public sectors, as well as the ever-changing regulatory landscape, can create uncertainty and volatility in the market. This can make it challenging for businesses to plan and invest for the long term, potentially hindering economic stability and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of a mixed market economy?
A mixed market economy is an economic system that combines elements of a market economy with elements of a planned or command economy.
What are the features of a mixed market economy?
Features include private ownership of resources, government intervention, competition, and consumer choice.
What is the role of government in a mixed market economy?
The government plays a role in regulating markets, providing public goods and services, and addressing market failures.
What are the advantages of a mixed market economy?
Advantages include flexibility, innovation, consumer choice, and a safety net for those in need.
What are the disadvantages of a mixed market economy?
Disadvantages include income inequality, potential for government failure, and market inefficiencies.
How does a mixed market economy balance private and public ownership?
A mixed market economy allows for both private ownership of resources (such as businesses and property) and public ownership of certain goods and services (such as infrastructure and education).
How does a mixed market economy differ from a purely capitalist or socialist economy?
A mixed market economy combines elements of both capitalism and socialism, allowing for some government intervention while still maintaining a level of private ownership and free market competition.